Here is a summary and a flowchart for The Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989, based on the provided “Arrangement of Sections”.
🧾 Summary of Chapters
Chapter I – Preliminary
Basic structure: Title, definitions.
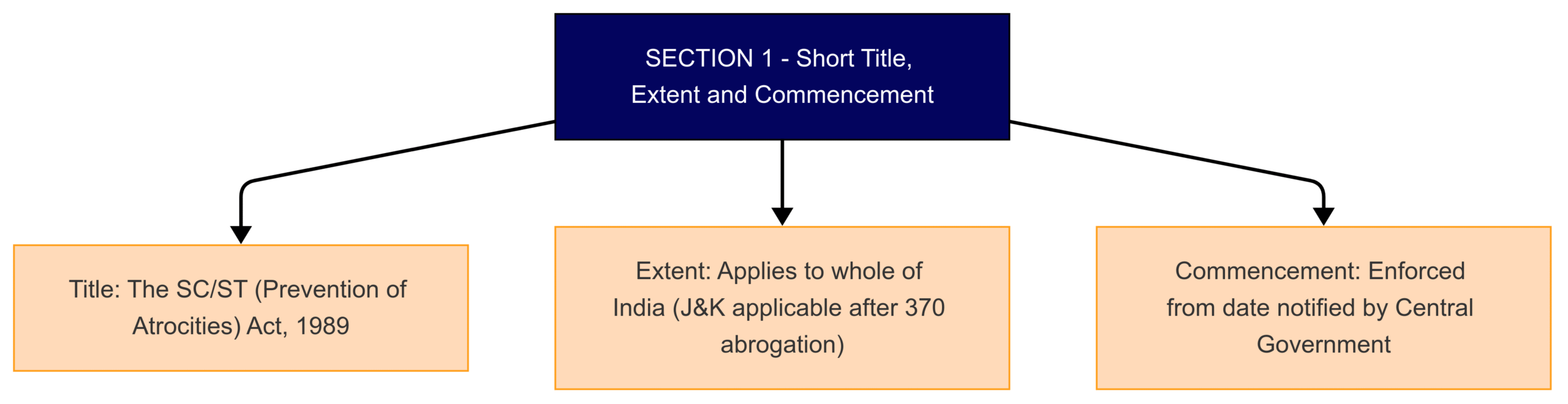
Section 1: Provides the title of the Act, its territorial extent (whole of India except J&K as per original text), and commencement date.
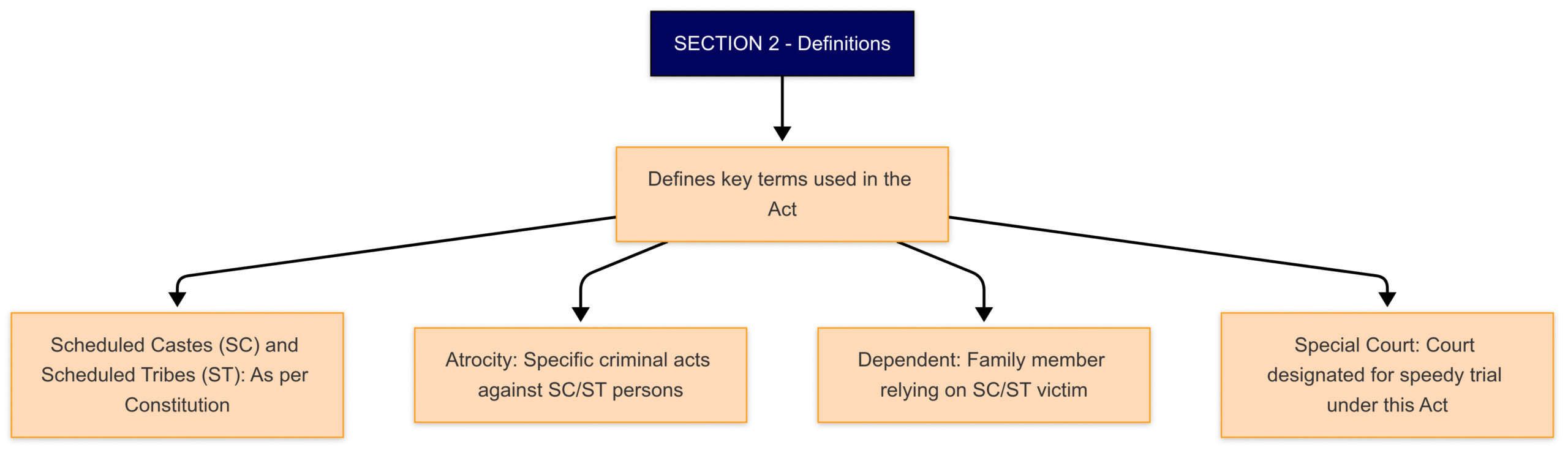
Section 2: Defines important terms used in the Act such as “Scheduled Castes”, “Scheduled Tribes”, “atrocity”, etc.
Chapter II – Offences of Atrocities
- Defines atrocities, their punishments, responsibilities of public servants, legal presumptions, and power conferrals.
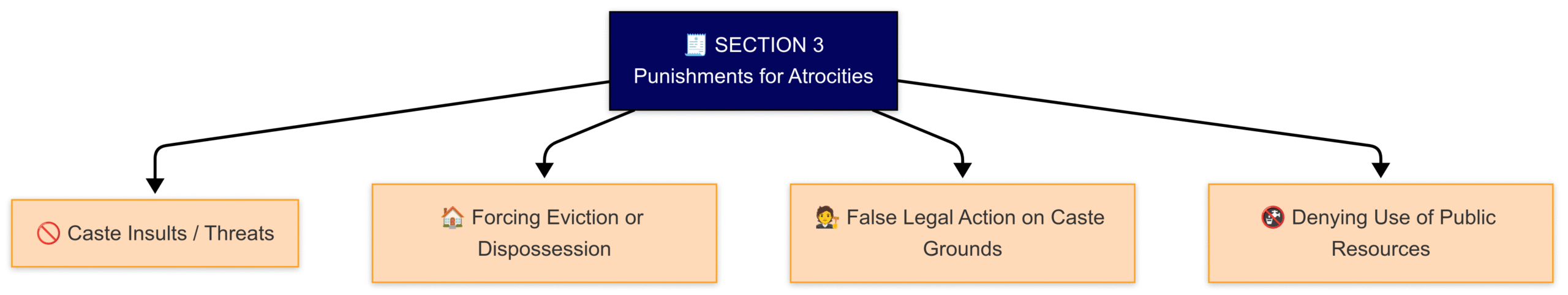
Section 3- Punishments for offences of atrocities
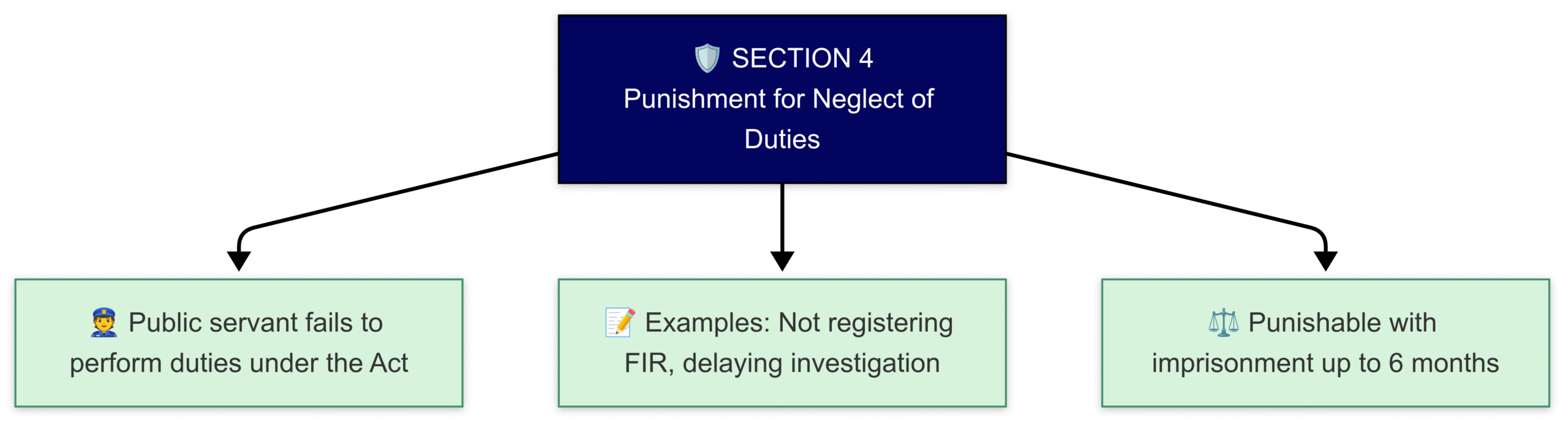
Section 4 of SC/ST Act
🔹 Section 4 – Neglect by Public Servants
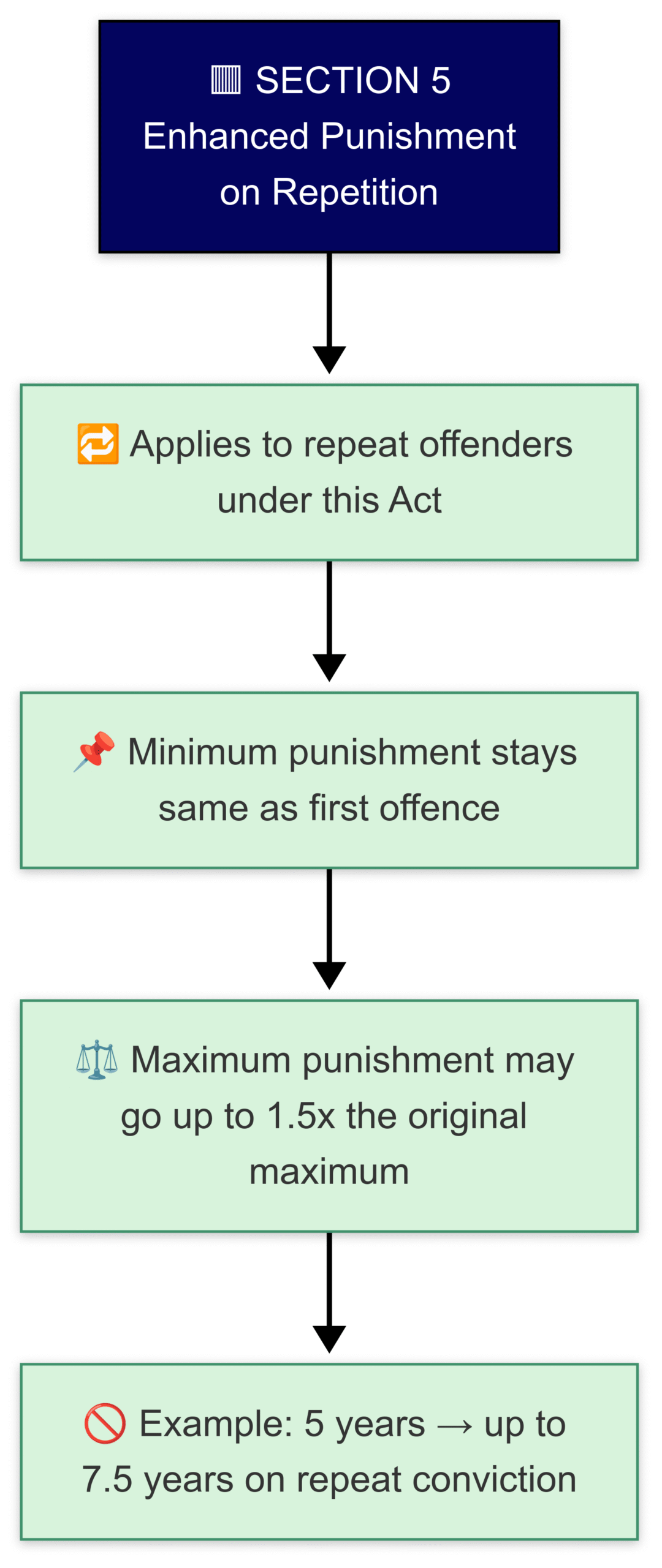
Section 5 of SC/ST Act
Section 5 – Harsher Punishment for Repeat Offenders
If someone commits an offence again after being convicted once, they’ll face increased punishment the second time.
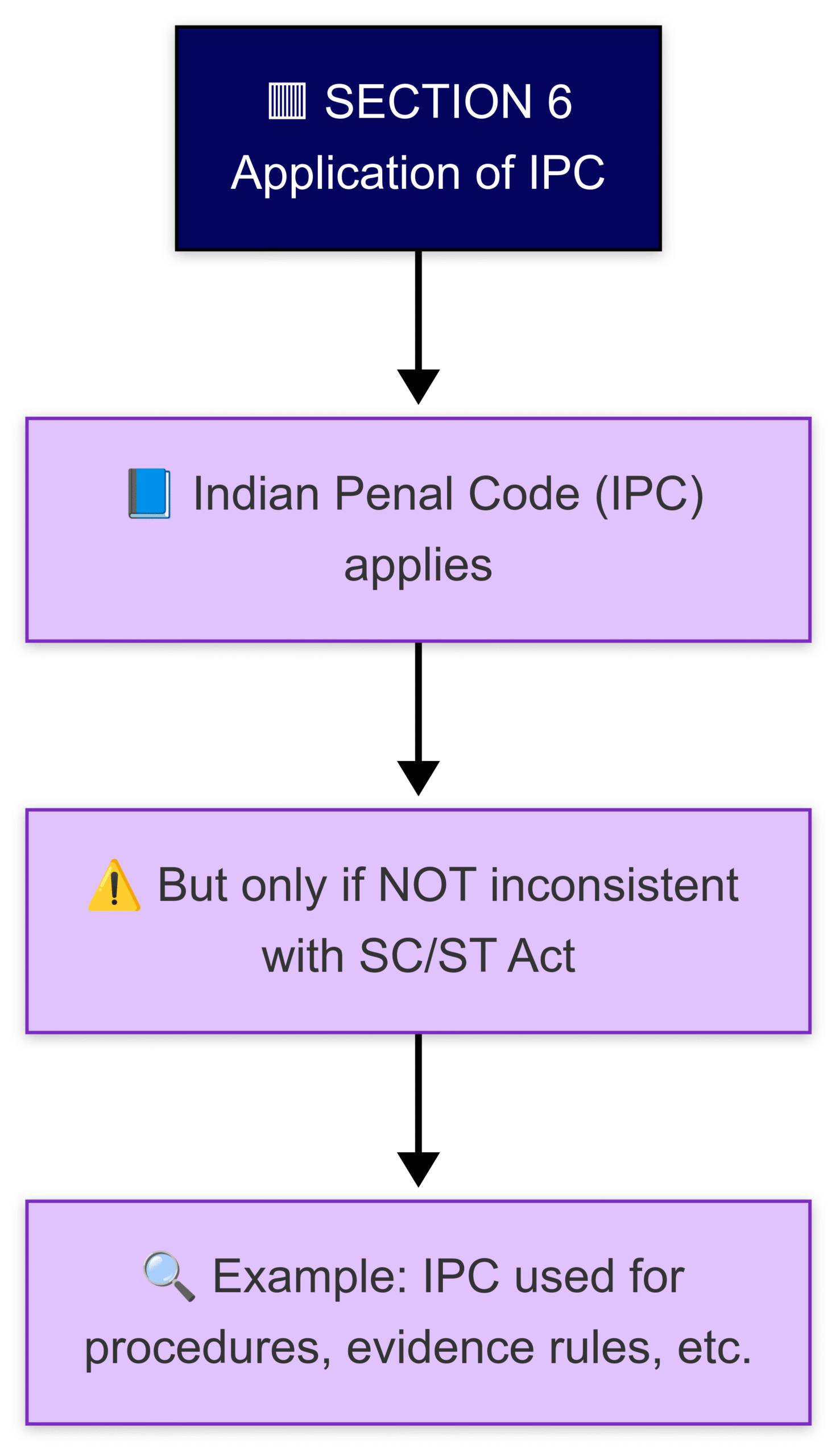
Section 6 – Use of IPC (Indian Penal Code)
The IPC applies to situations under this Act unless it contradicts the provisions of this law.
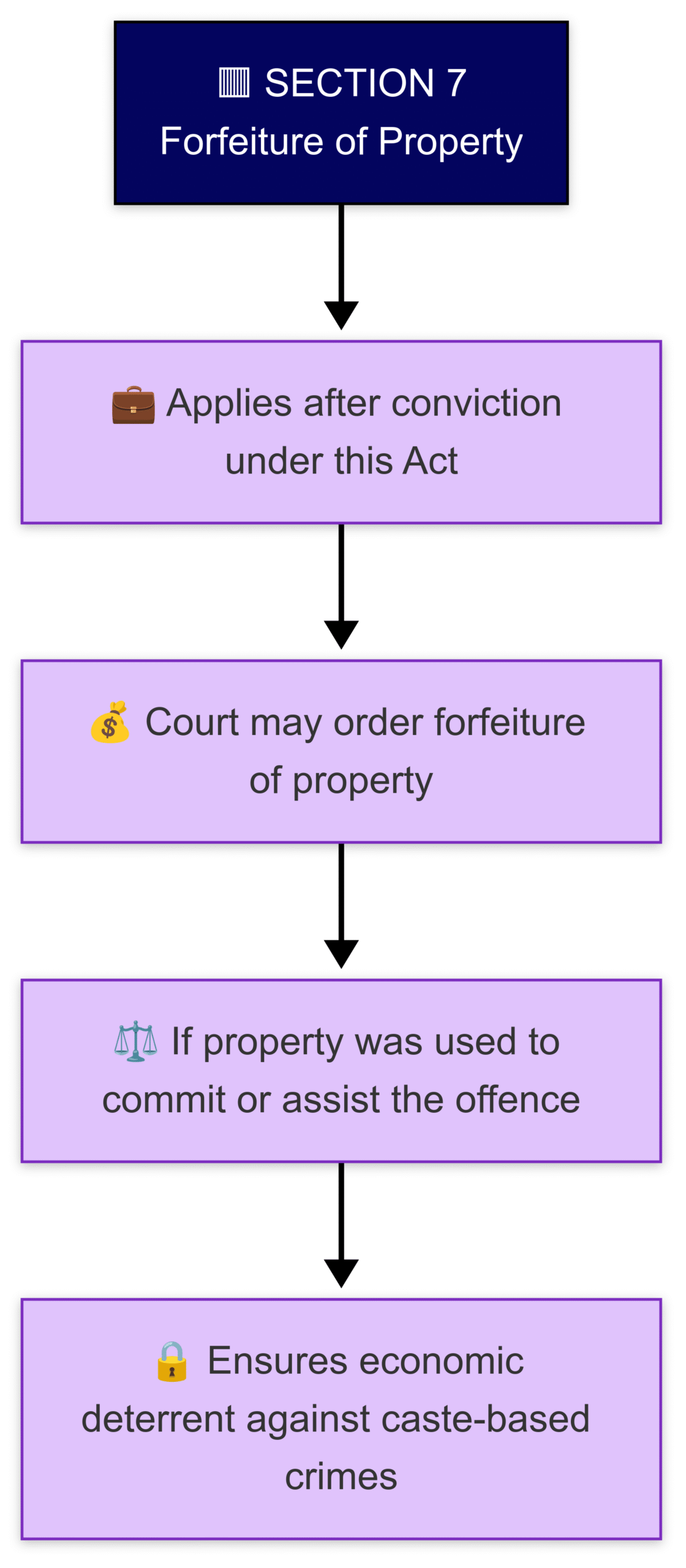
Section 7 – Forfeiture of Property
Courts can order seizure of property used to commit or aid any offence under this Act.
Section 8 – Presumption of Caste-based Offence
If the accused knew the victim belongs to SC/ST, it is assumed the offence was caste-based, unless proven otherwise by the accused.
Section 9 – Delegation of Powers
Government can authorize specific officers to implement this Act: to investigate, arrest, and prosecute offenders.
Section 10 – Removal (Externment) of Habitual Offenders
If someone is likely to commit an atrocity again, the District Magistrate can order them to stay away from a certain area for up to 2 years.
Chapter III – Externment
- Legal procedures for removing repeat or likely offenders from areas to prevent atrocities.
Chapter IV – Special Courts
- Establishes exclusive courts and prosecution mechanisms for speedy justice.
Chapter IVA – Rights of Victims and Witnesses
- Ensures protection, rights, and support for victims and witnesses.
Other Provisions
- Preventive measures, override of general laws, prohibition of anticipatory bail, collective fines, and rulemaking power.