Skip to content
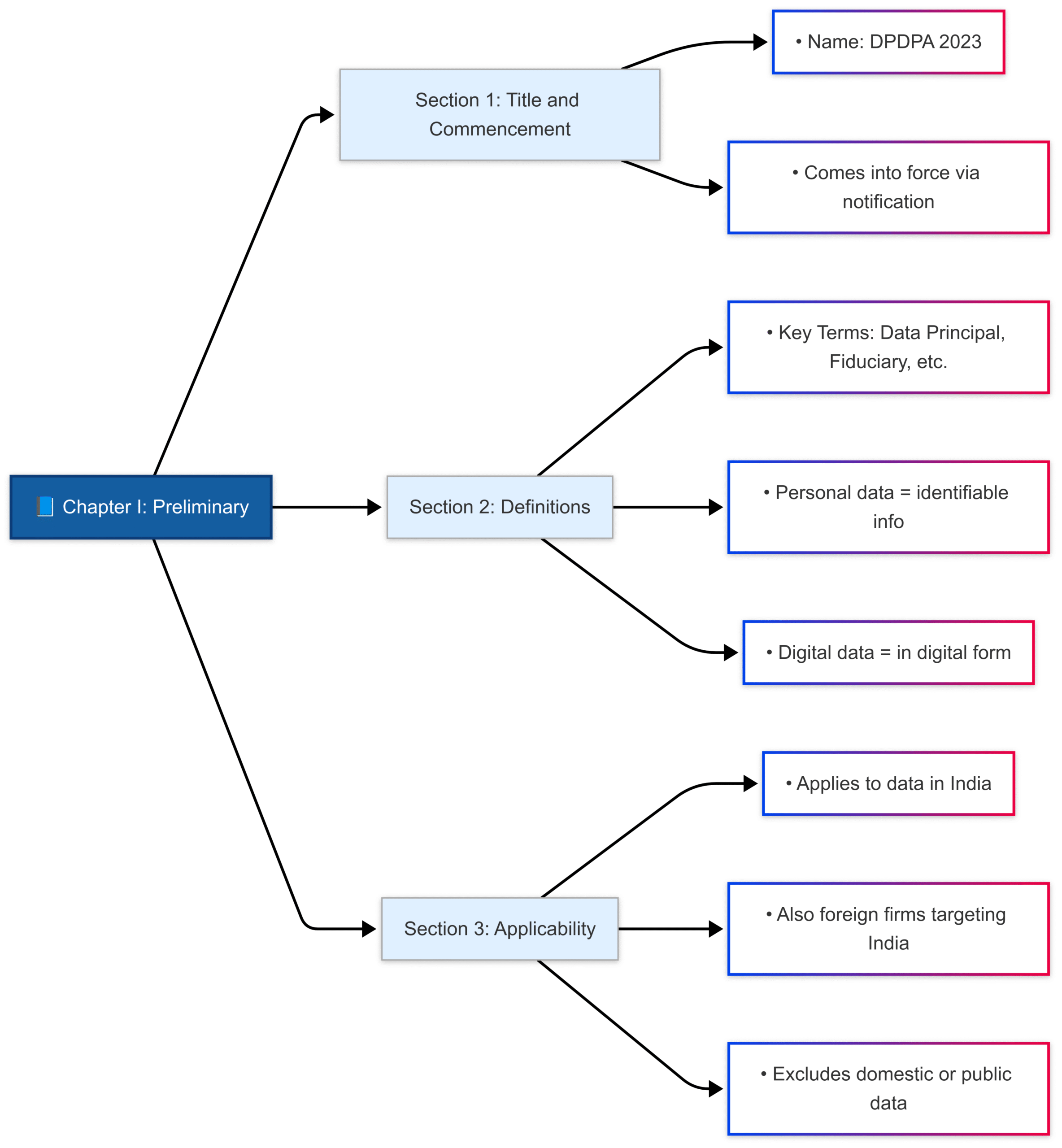
CHAPTER I: Preliminary
- Defines key terms like Data Principal, Data Fiduciary, Consent Manager, etc.
- Applicability: Applies to processing of digital personal data in India and abroad (if offering goods/services in India).
- Exemptions: Does not apply to domestic/personal use or data made public by law or the Data Principal.
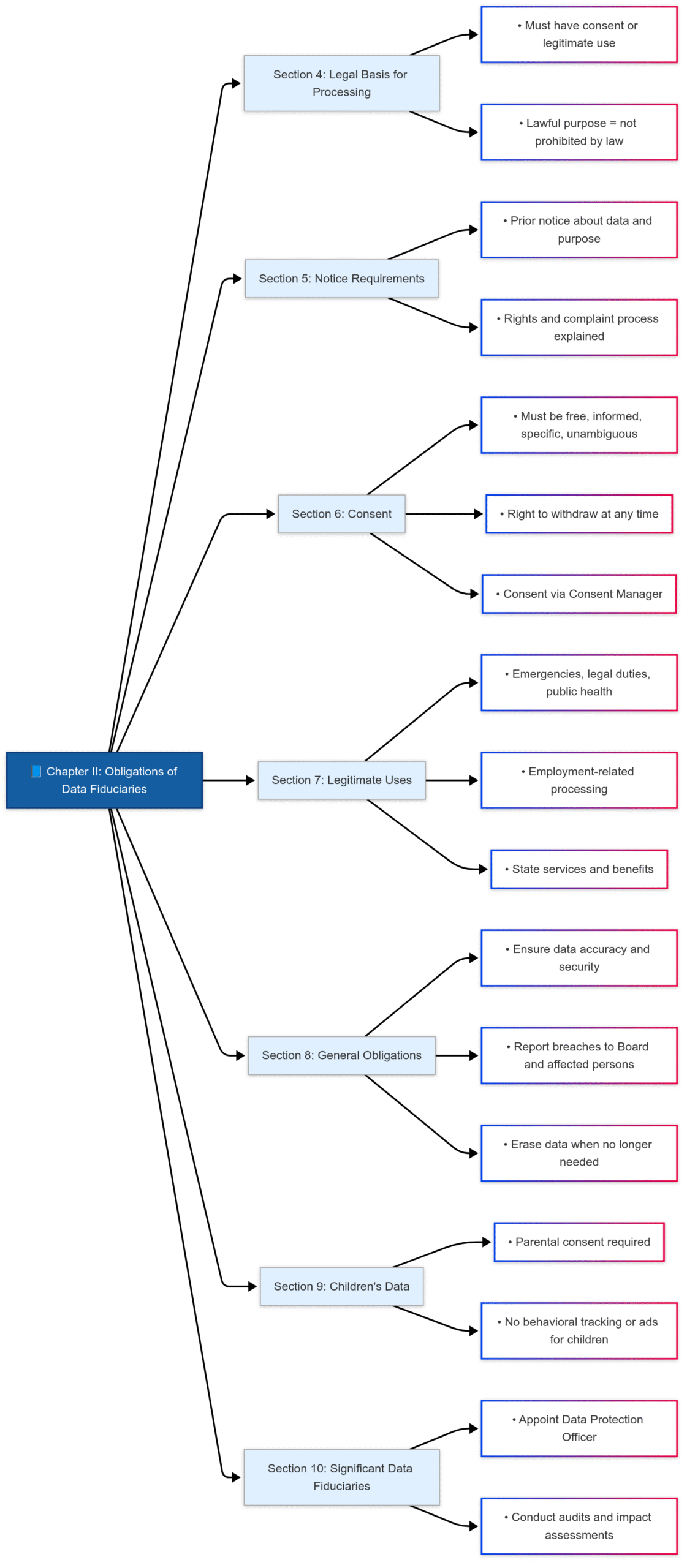
CHAPTER II: Obligations of Data Fiduciaries
- Lawful Processing: Must be based on consent or legitimate use.
- Notice: Must inform Data Principal about purpose and rights before obtaining consent.
- Consent: Must be free, specific, informed, and unambiguous.
- Legitimate Uses: Includes emergencies, legal obligations, public health, employment, etc.
- Security & Retention: Fiduciaries must protect data, report breaches, and erase data when no longer needed.
- Children’s Data: Requires verifiable parental consent and prohibits behavioral tracking/ads for children.
- Significant Data Fiduciaries: Must appoint Data Protection Officers and conduct audits/impact assessments.
CHAPTER III: Rights and Duties of Data Principal
- Right to Information: Know what data is processed and with whom it is shared.
- Right to Correction & Erasure: Can update or delete their data.
- Grievance Redressal: Right to an accessible mechanism to lodge complaints.
- Right to Nominate: Can assign someone to act on their behalf in case of death/incapacity.
- Duties: Must provide accurate data, avoid impersonation, and refrain from frivolous complaints.
CHAPTER IV: Special Provisions
- Cross-border Data Transfer: Can be restricted by government notification.
- Exemptions: For legal proceedings, law enforcement, research, state security, and financial defaults.
- Startup Relief: Certain provisions can be relaxed for startups by government notification.
CHAPTER V: Data Protection Board of India
- Establishment: An independent board to enforce the Act.
- Powers: Inquire into breaches, impose penalties, oversee compliance.
- Structure: Comprises Chairperson and Members appointed by the Central Government.
CHAPTER VI: Powers, Functions & Procedure of the Board
- Inquiry: Can summon, inspect, and order actions after due process.
- Digital Office: Board functions digitally for complaint receipt and hearings.
- Assistance: May seek help from law enforcement or government officers.
CHAPTER VII: Appeals & Dispute Resolution
- Appeals: Orders can be challenged before the Telecom Appellate Tribunal within 60 days.
- Mediation: Disputes may be referred for mediation.
- Voluntary Undertaking: Board can accept corrective commitments from violators.
CHAPTER VIII: Penalties and Adjudication
- Penalties: Up to ₹250 crore for certain violations.
- Factors: Gravity, duration, gain/loss, intent, and impact are considered while imposing penalties.
- Fund: All penalties go to the Consolidated Fund of India.
CHAPTER IX: Miscellaneous
- Legal Immunity: Good-faith actions under the Act are protected.
- Supremacy: Overrides conflicting laws.
- Jurisdiction Bar: Civil courts can’t intervene in matters under the Act.
- Rulemaking: Central Government empowered to make rules.
- Amendments: Updates to other Acts like the IT Act, RTI Act, and TRAI Act are included.