Article 6 of Indian Constitution: Rights of citizenship of certain persons who have migrated to India from Pakistan
Article 6 Rights of citizenship of certain persons who have migrated to India from Pakistan – Constitution Of India.

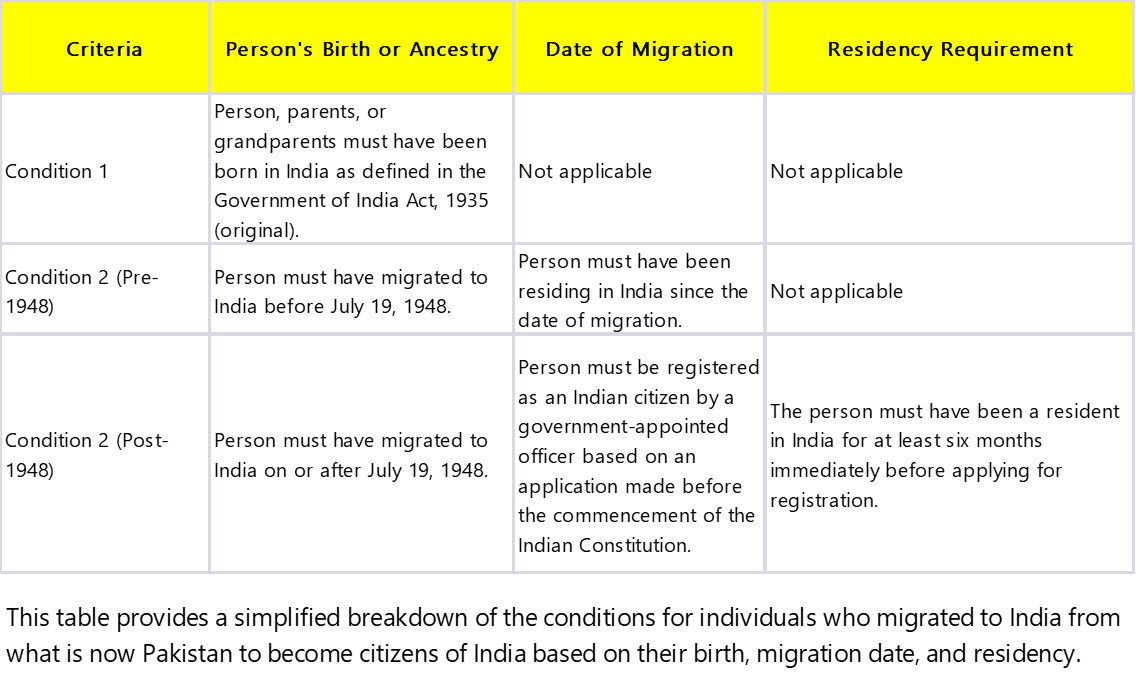
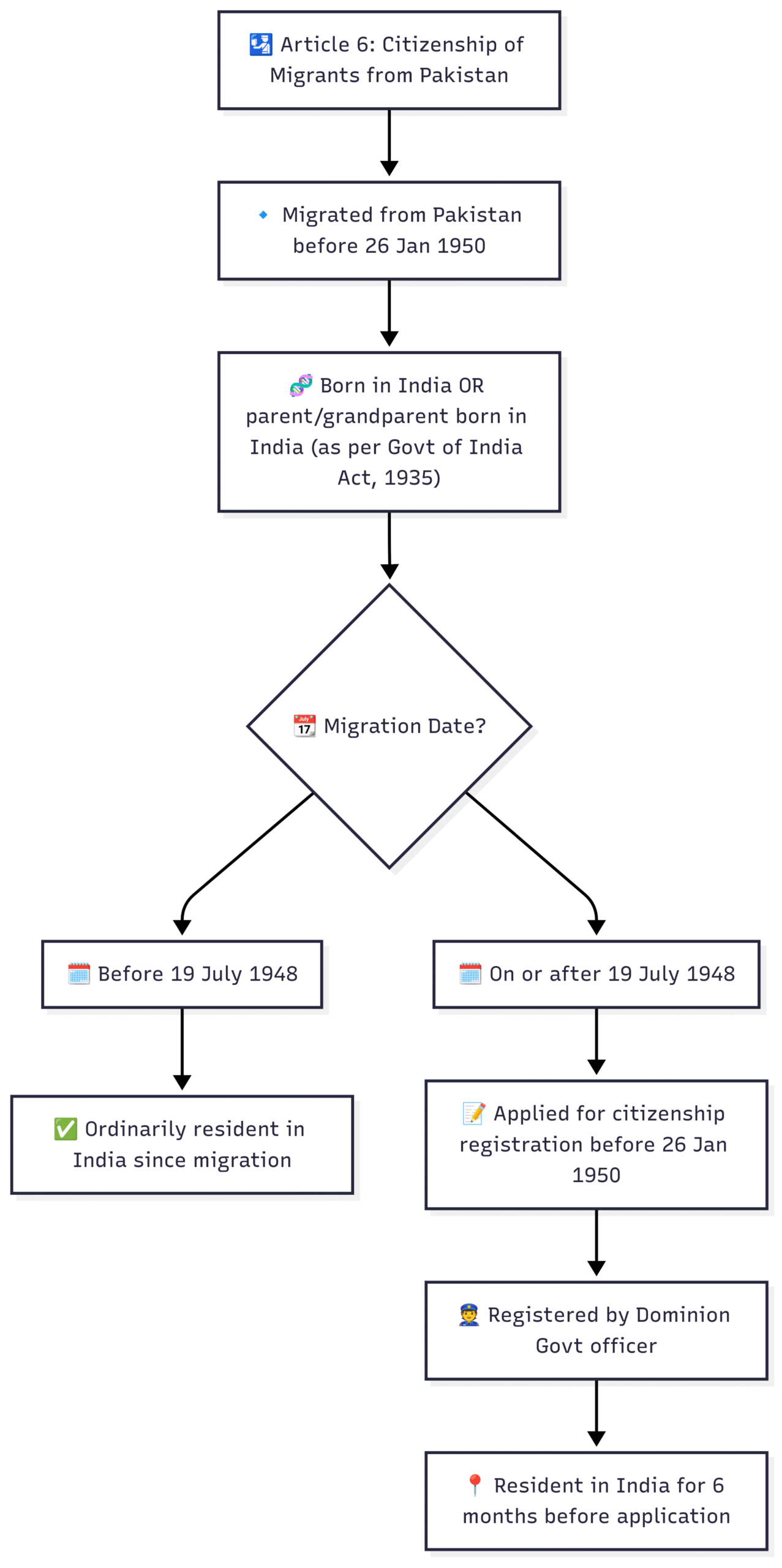
Notwithstanding anything in article 5, a person who has migrated to the territory of India from the territory now included in Pakistan shall be deemed to be a citizen of India at the commencement of this Constitution if— a). he or either of his parents or any of his grandparents was born in India as defined in the Government of India Act, 1935 (as originally enacted); and b) (i). in the case where such person has so migrated before the nineteenth day of July, 1948, he has been ordinarily resident in the territory of India since the date of his migration, or (ii) in the case where such person has so migrated on or after the nineteenth day of July, 1948, he has been registered as a citizen of India by an officer appointed in that behalf by the Government of the Dominion of India on an application made by him therefor to such officer before the commencement of this Constitution in the form and manner prescribed by that Government: Provided that no person shall be so registered unless he has been resident in the territory of India for at least six months immediately preceding the date of his application.
Summary on Article 6 of the Indian Constitution
FAQs on Article 6 of the Indian Constitution
Q1: What is Article 6 of the Indian Constitution about? A1: Article 6 of the Indian Constitution deals with the rights of citizenship for certain persons who migrated to India from Pakistan.
Q2: Who does Article 6 apply to? A2: Article 6 applies to individuals who migrated to India from Pakistan during or after the partition in 1947.
Q3: What rights does Article 6 provide to these individuals? A3: Article 6 provides certain rights of citizenship to individuals who migrated from Pakistan to India. It specifies that such individuals shall be deemed to be citizens of India if they or their parents or grandparents were born in India as defined in the Government of India Act, 1935.
Q4: What is the significance of being deemed a citizen under Article 6? A4: Being deemed a citizen under Article 6 confers the rights and privileges of Indian citizenship, including the right to vote, the right to hold public office, and the right to access government services and benefits.
Q5: Are there any conditions or requirements for acquiring citizenship under Article 6? A5: Yes, to acquire citizenship under Article 6, it is necessary for the individual or their parents or grandparents to have been born in India as defined in the Government of India Act, 1935.
Q6: Is there a specific time period mentioned in Article 6 for migration from Pakistan? A6: Article 6 does not specify a specific time period for migration from Pakistan. It applies to individuals who migrated to India from Pakistan during or after the partition in 1947.
Q7: Can individuals who migrated from Pakistan before 1947 avail the rights of citizenship under Article 6? A7: No, Article 6 specifically applies to individuals who migrated from Pakistan during or after the partition in 1947. It does not cover individuals who migrated from Pakistan before that period.
Q8: Can Article 6 be amended? A8: Yes, Article 6 can be amended through the constitutional amendment process, which requires the approval of both houses of Parliament and ratification by the majority of state legislatures. However, any amendments should be consistent with the principles of citizenship and the rights of individuals covered under Article 6.
Q9: Does Article 6 cover individuals who migrated from countries other than Pakistan? A9: No, Article 6 specifically deals with individuals who migrated from Pakistan to India. It does not extend to individuals who migrated from countries other than Pakistan.
Q10: Are there any legal challenges or interpretations related to Article 6? A10: While there may have been legal challenges or interpretations related to Article 6, specific details would depend on the specific cases or circumstances. Legal challenges and interpretations are typically addressed by the courts to ensure compliance with the constitutional provisions.